GALLSTONES
What is the purpose of the gallbladder ?
The gallbladder is a reservoir for bile produced by the liver. During meals it empties its content into the bowel to help digest fats. Removal of the gallbladder is without long-term consequence.
What causes gallstones ?
Women are 2-3 times more likely than men to develop stones because of female sex hormones, pregnancy and oral contraception. Rapid weight loss secondary to dieting or surgery for obesity can also be associated with gallstones. In rare cases stones are the result of an inherited metabolic disease.
What are gallstones made of ?
Cholesterol is the most common component, followed by bilirubin produced by haemoglobin metabolism. Calcium can make gallstones visible on plain radiographs but the only reliable exam is abdominal ultrasound.
What are the risks of having gallstones ?
The presence of stones within the gallbladder may be the cause of intermittent pain (biliary colic) or other more serious manifestations: acute and chronic inflammation (cholecystitis) and the passage of a stone from the gallbladder into the common bile duct. The latter may result in jaundice, biliary infection and acute pancreatitis. Pancreatitis is a self-sustaining process that can be life-threatening in 10% of cases.
Why opt for surgery ?
-
Once a patient starts having symptoms chances are high that they will recur and worsen with time.
-
Frequent travellers may be concerned about being ill while abroad.
-
Surgery is easier and safer when performed before the occurrence of complications.
-
Non-operative techniques such as chemical dissolution and ultrasonic fragmentation of stones have not proved effective.
How is surgery done ?
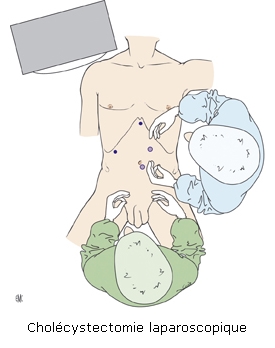
The gallbladder is removed along with the stones. There is no point in removing only the stones because others would develop. Minimally invasive surgery using four 5-10mm incisions is the standard technique. It takes less than 1 hour and the patient returns home the following day.
Patients feel bloated for several days and may have transient shoulder pain due to the presence of abdominal gas. Over the counter pain medications such as paracetamol are usually sufficient and can be combined with nonsteroïdal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen,Brufen,Diclofenac) in case of shoulder pain. Showering is allowed and waterproof dressing do not have to be changed before the first office visit 1 week later.
Normal activities such as walking, going up stairs and driving are permitted immediately. Avoiding strenuous exercise involving abdominal straining is advised for 4-6 weeks. Work leave is usually 1-2 weeks.
|
|
 |
|
| FIG : minimally invasive cholecystectomy
|
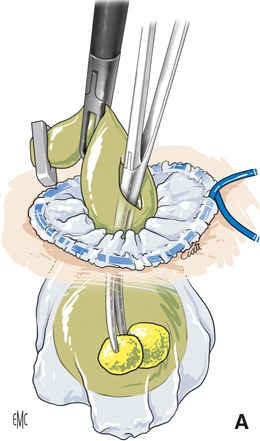
Fig : Extraction of the gallbladder in a bag at the level of the umbilicus. Source : F Borie Cholécystectomie et exploration de la voie biliaire principale par coelioscopie. Traitement coelioscopique de la lithiase de la voie biliaire principale EMC-Techniques chirurgicales-Appareil digestif 2014 ;9(3) :1-21 Article 40-950 |
Symptoms to watch for after surgery:
- Increasing abdominal or back pain
- Fever > 37.8°
- Jaundice
- Pain redness and swelling of the umbilicus, usually due to a benign trocar site infection
Should you notice these signs you are advised to contact your family doctor or surgeon.
How much will it cost me ?
In accordance with Belgian legislation the disposables (scissors, trocars, sealing devices) are charged 110 €. If you have private insurance this amount will be covered by your insurance.
Dr Serge Landen - www.drlanden.be