OBESITY SURGERY
In developed countries a quarter of the population is overweight and this now stands out as the most significant challenge to public health in the coming years. Severe obesity also called morbid obesity concerns 5% of the population and is defined as a body mass index equal or superior to 35. Body Mass Index can be calculated by dividing an individual’s weight by the square of his height in metres. (weight (kg) / height (m)²)
A BMI of 35 can negatively impact health :
 diseases such as hypertension, arteriosclerosis, diabetes, arthritis and cancer are likelier
diseases such as hypertension, arteriosclerosis, diabetes, arthritis and cancer are likelier- life expectancy is decreased
- quality of life is poorer
- health costs are increased
In severely obese individuals the traditional measures such as diet, exercise and behavioural therapy have been shown to be ineffective in achieving durable weight loss. Aside from the costs involved patients often become discouraged seeing that their efforts are not rewarded. At that point the patient can either accept his condition or recourse to surgery.
Among the various surgical procedures, gastic banding is one that reduces the volume of food that can be ingested. Gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy involve other mechanisms such as malabsorption and cerebral inhibition in addition to food volume reduction. All can be performed by a minimally invasive approach. (keyhole)
GASTRIC BANDING is easiest to perform, requiring just an overnight stay in hospital. It can be adjusted during office visits according to weight loss and food tolerance. Loss of 50% of excess weight can be expected after 2 years. Failures (20%) as defined by insufficient weight loss are due inadequate eating habits and less frequently to band displacement. Long term postoperative follow-up is essential.
|
* Gastric bypass |
* Sleeve Gastrectomy |
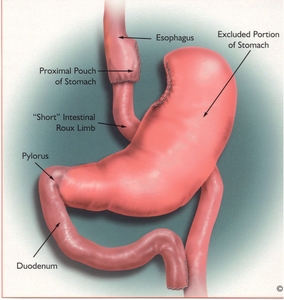
GASTRIC BYPASS reduces the stomach volume but also length of small bowel involved with food absorption. It is a more elaborate procedure and requires a 3-4 day hospitalization. It is particularly indicated in patients with heartburn, nibblers as opposed to bulk eaters, sweet eaters and patients unwilling to accept any alimentary constraints. It is also used following failed gastric banding. Weight loss is superior to gastric banding and patients can expect to loose 60-75% of excess weight within 6 months after surgery.
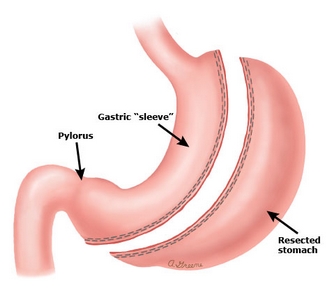
SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY yields similar results to gastric bypass but is simpler to perform.
|
|
Gastric Band |
Gastric Bypass | Sleeve Gastrectomy |
| Hospital stay | 2 days | 3 days | 3 days |
| Risk of surgery |
very low |
low | low |
| Excess weight loss |
50% within 2 yrs | 60-75% / 6 months | 60-75% / 6 months |
| Eating pleasure |
medium-good | good | good |
| Vit. deficiencies |
rare | supplements needed | rare |
Surgery often brings spectacular improvement of patients’ physical and psychological well-being. Diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipemia, poor sleep caused by snoring and joint pain improve or disappear within weeks and months, enabling the patient to engage in physical activity. Self esteem is boosted along with social life and professional activity.
Patients are taken charge of before and after surgery by our centre at DELTA hospital dedicated to obesity. The centre groups in a single location all the specialists that are involved in the treatment of obesity allowing a global and personalized approach to each patient. At present more than 500 patients are operated each year which makes it the largest referral centre in Belgium.
Figures courtesy of Johnson & Johnson
Dr Serge Landen - www.drlanden.be